
Hello and welcome back to another in-depth exploration of strategies that can elevate your online income.
Today, we’re focusing on Pay Per Lead (PPL), a performance-based model that has proven itself as a vital tool for both affiliates and advertisers.
If you’re searching for ways to optimize your affiliate marketing efforts or generate high-quality leads for a business, this guide is designed to provide all the details you need to succeed with PPL in 2025 and beyond.
For those new to my work, I’m Ali, a veteran affiliate marketer with over a decade of experience running high-traffic websites through my company, AFFiNCO.
Starting from small-scale campaigns, I’ve grown a network of successful sites by mastering methods like PPL. This approach has been a consistent performer in my portfolio, and I’m here to share practical knowledge, technical insights, and real-world applications to help you unlock its potential.
Defining Pay Per Lead (PPL)
Pay Per Lead (PPL) is an affiliate marketing model where payments are tied to the generation of leads rather than clicks or completed sales. A lead refers to a potential customer who expresses interest in a product or service by completing a predefined action.
Examples include submitting a contact form, signing up for a newsletter, requesting a quote, or registering for a trial.
To break it down simply:
In PPL, affiliates earn commissions for delivering these leads, regardless of whether the lead converts into a paying customer. This distinguishes it from other models and makes it appealing for businesses seeking cost-effective lead generation and affiliates aiming for reliable income.
For advertisers, PPL ensures payments are made only for actions that show genuine interest, making it a budget-friendly option. For affiliates, it simplifies the process by focusing on driving engagement rather than navigating the full sales funnel.
This balance of efficiency and profitability is why PPL stands out in affiliate marketing.
How Pay Per Lead Works: A Detailed Process
Understanding the step-by-step mechanics of PPL is key to implementing it effectively. Here’s a breakdown of how it operates:
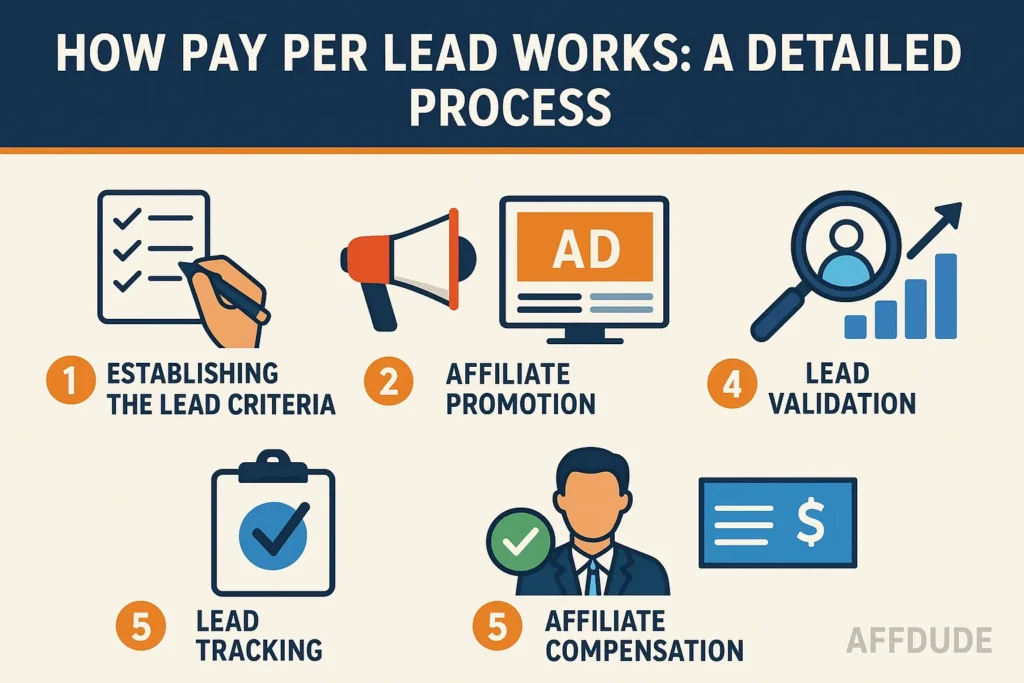
Step 1: Establishing the Lead Criteria
The process begins with the advertiser defining what qualifies as a lead. This varies by industry and business goals. Common examples include:
The action must be specific, trackable, and aligned with the company’s objectives to ensure the lead has value.
Step 2: Affiliate Promotion
Affiliates then promote the offer using various marketing channels. Options include:
The aim is to drive users to complete the action defined by the advertiser.
Step 3: Lead Tracking
When a user performs the desired action, such as submitting a form, a tracking system logs the event and credits the affiliate. This is achieved through:
Accurate tracking ensures affiliates receive proper credit for their efforts.
Step 4: Lead Validation
Advertisers assess lead quality to confirm they meet standards. Validation methods include:
This step ensures payments are made only for legitimate leads.
Step 5: Affiliate Compensation
Once validated, affiliates receive a fixed commission per lead. Payouts depend on the industry and lead value:
The agreed-upon rate is set within the affiliate program’s terms, ensuring transparency.
This structured process benefits both parties: advertisers gain interested prospects, and affiliates earn for their marketing efforts.
Why PPL Excels for Advertisers and Affiliates
PPL offers unique advantages that make it a standout choice. Let’s examine its value for both sides.
Advantages for Advertisers
Advantages for Affiliates
This mutual benefit drives PPL’s popularity in affiliate marketing.
Comparing PPL to Other Affiliate Models
To appreciate PPL’s strengths, let’s compare it to Pay Per Click (PPC) and Pay Per Sale (PPS).
Pay Per Click (PPC)
Pay Per Sale (PPS)
Pay Per Lead (PPL)
For instance, a finance company seeking loan applicants would prefer PPL over PPC for its focus on intent, while an online store might choose PPS for direct sales.
Overcoming PPL Challenges
PPL has hurdles, but they’re manageable:
Proactive steps keep PPL effective.
Key Metrics for PPL Success
Track these to measure performance:
Tools like Google Analytics or CRM platforms provide these insights.
Conclusion: PPL’s Lasting Value
Pay Per Lead is a proven affiliate marketing strategy. Advertisers gain efficient lead generation, while affiliates enjoy steady commissions. Its flexibility suits industries from finance to tech. With over ten years in this field, I’ve seen PPL deliver consistent results, and it remains a top choice for 2025.
Ready to try PPL? Begin with a test campaign, refine your approach, and scale up.
Questions? Drop them below—I’m here to assist. Happy marketing!






